Trails, Parks and Open Space
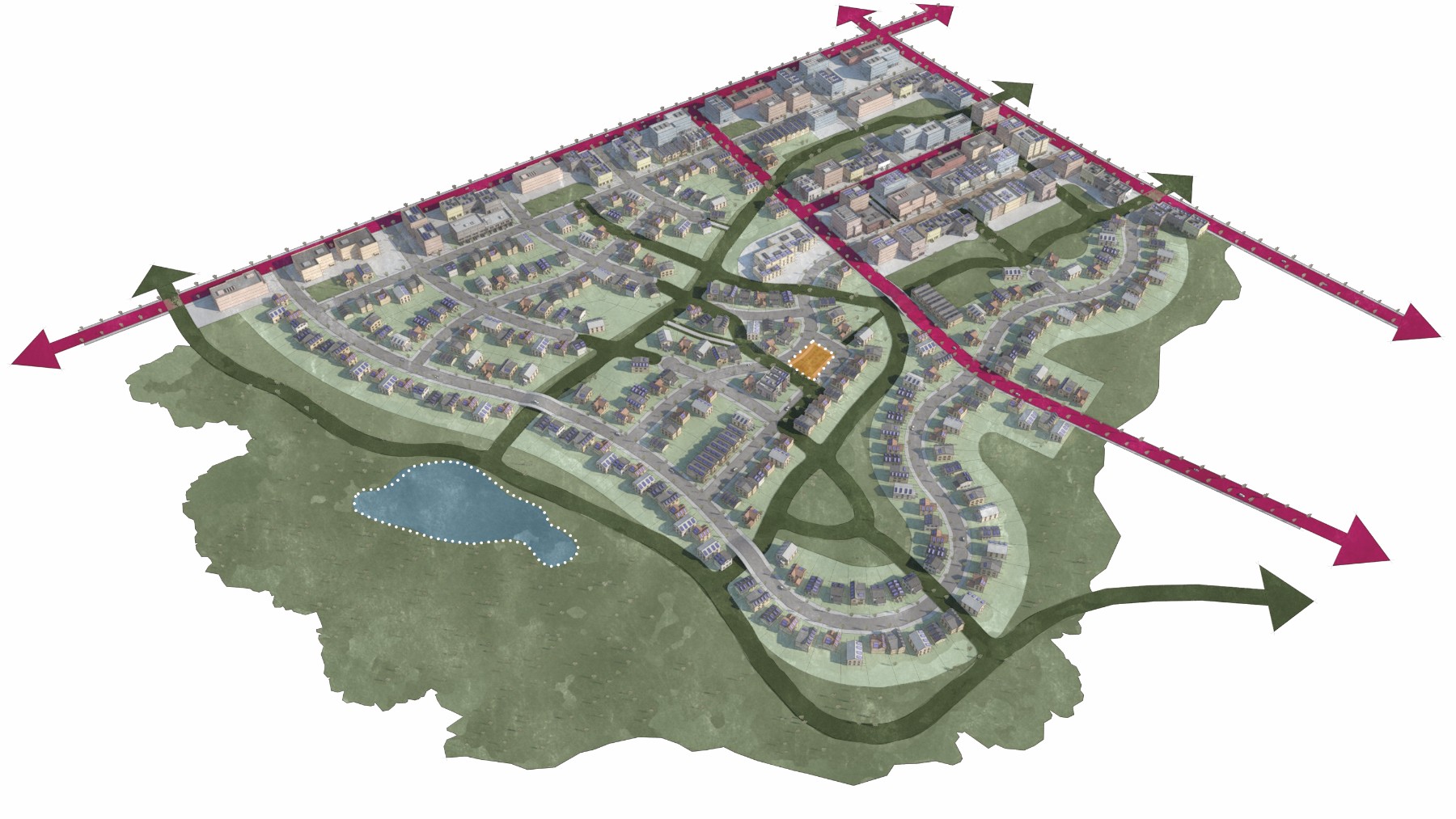
Green neighborhood
Introduction
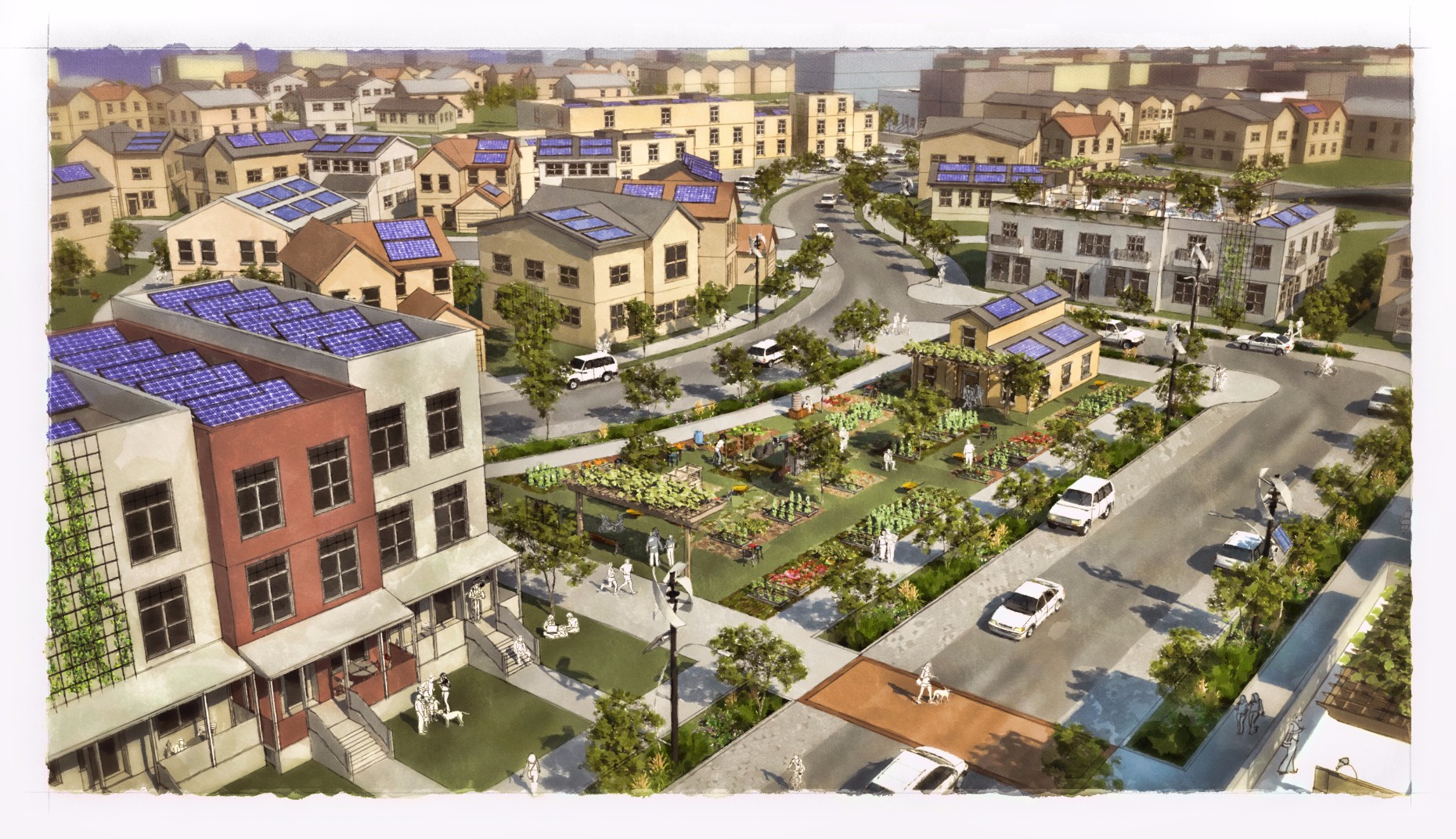
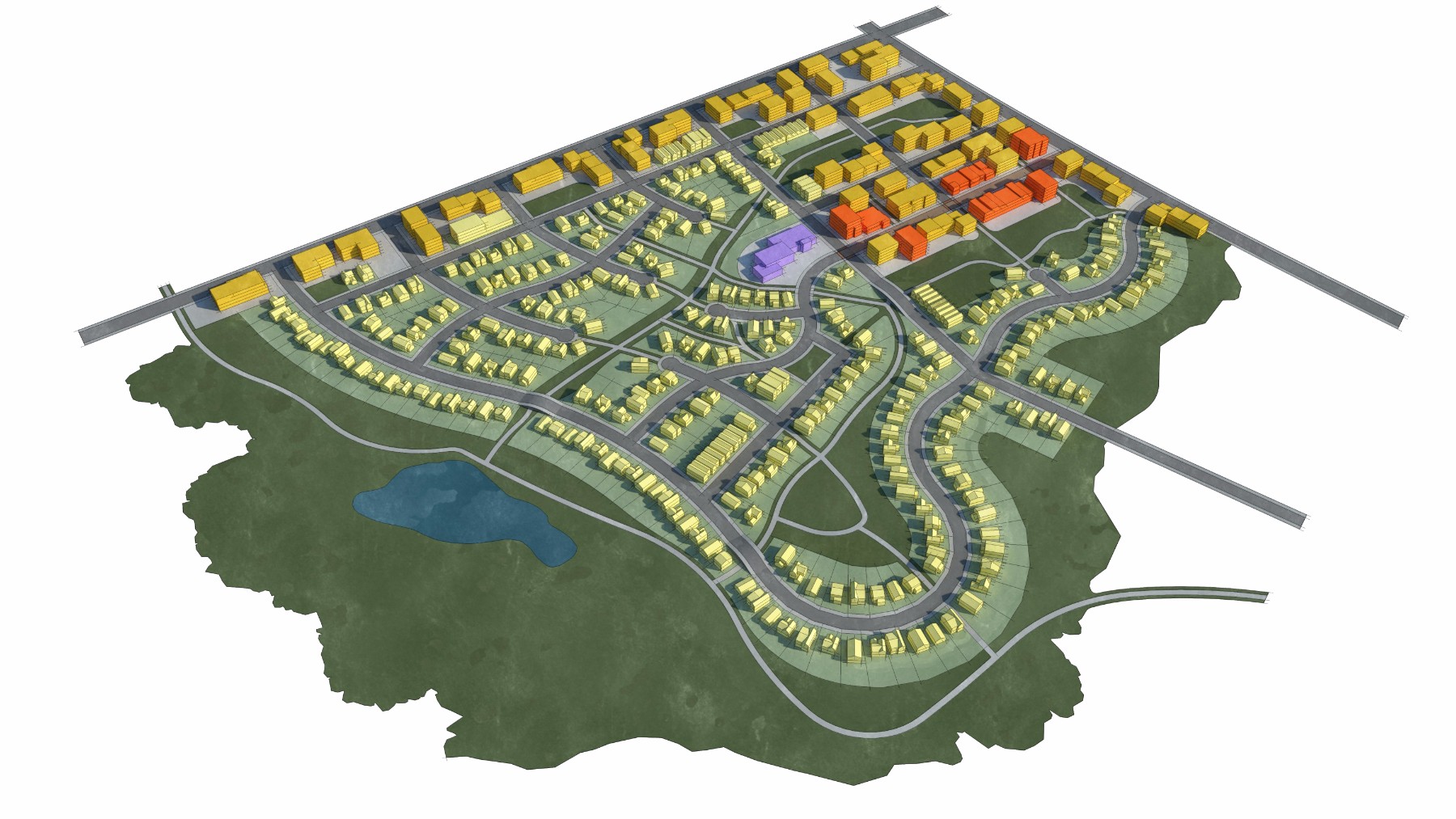
The Green Neighborhood place type typically involves new development focused on optimizing sustainability. Key features include the use of natural drainage ways, a network of connected pedestrian and bicycle trails, designated areas for urban agriculture, alternative energy production, localized utilities and site orientation for passive lighting, heating and cooling. The land use mix is mostly compact single-family residential with the potential for a mixed-use node. There are often a variety of small and larger park-like open spaces within the development. It’s common to use sustainable materials and technology such as solar panels, small wind turbines and low impact development practices. Potential locations for this could include Mahncke Park and areas outside Interstate Loop 410 in the southern portion of the city.
Major Determinant
New residential neighborhood development focused on sustainability and low impact development.
Relation to VIA Supportive Development Typologies
One of three typologies corresponding to VIA’s Urban Center typology.
Predominant Land Uses
Compact single-family residential with some mixed-use and/or smaller scale commercial.
Performance Standards
Height: 2 to 4-story development or 30 to 65 feet
Massing and Density: 10 to 20 housing units per acre and 0.5:1 to 2:1 Floor Area Ratio (FAR)
Street Level Activation: Transparency along primary street of 25%; transparency along side street of 15%
Connectivity: Maximum block perimeter of 1,000 feet; minimum 90 intersections per square mile
Public Space: Plazas and park spaces totaling 15 acres per 1,000 residents
Parking: On-street and off-street parking
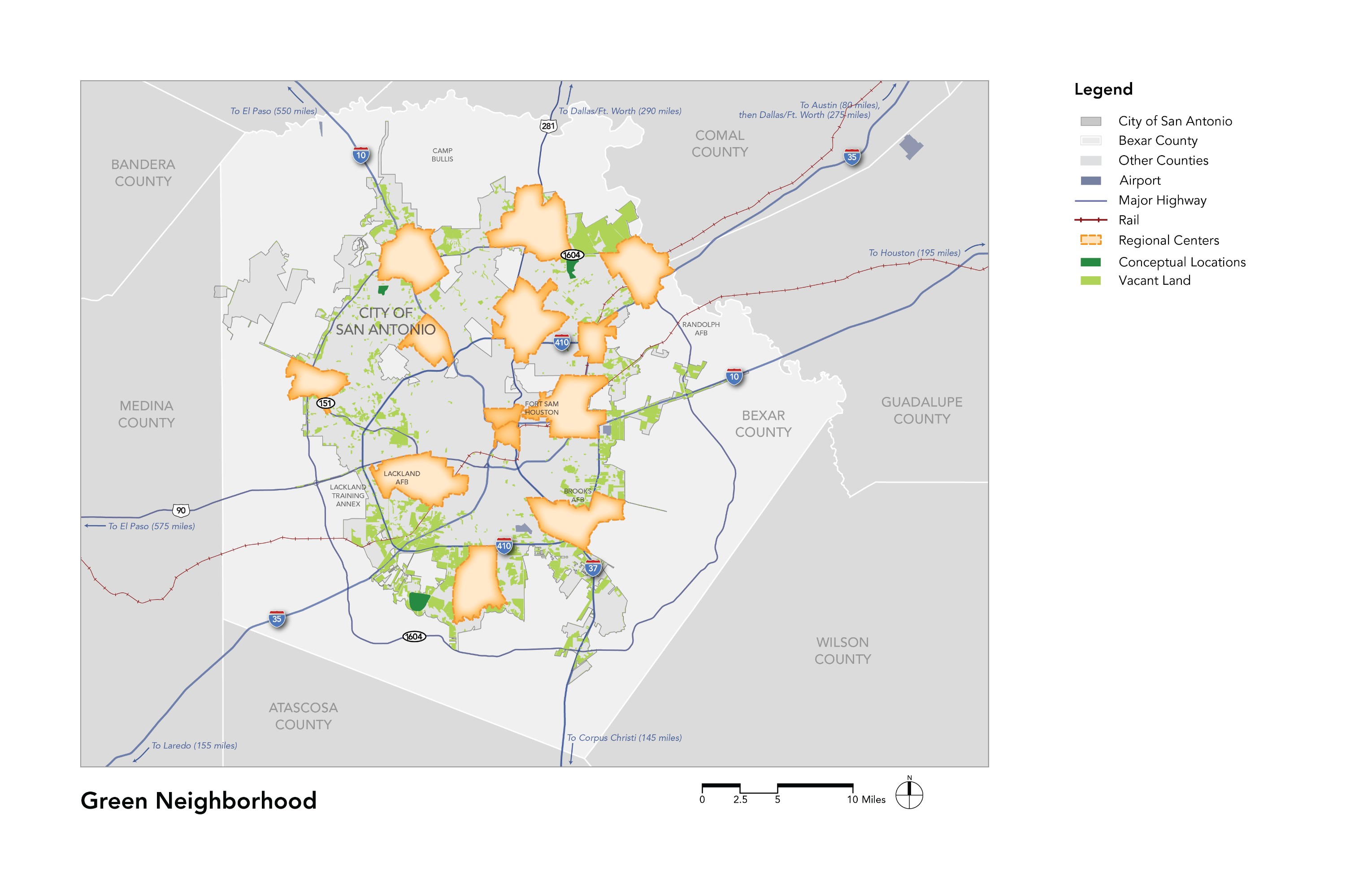
Potential Locations
The Green Neighborhood place type is all vacant areas of the city and especially in areas with natural open space or more sensitive landscapes. The map above depicts the majority of vacant parcels in San Antonio with an area of five acres or larger.