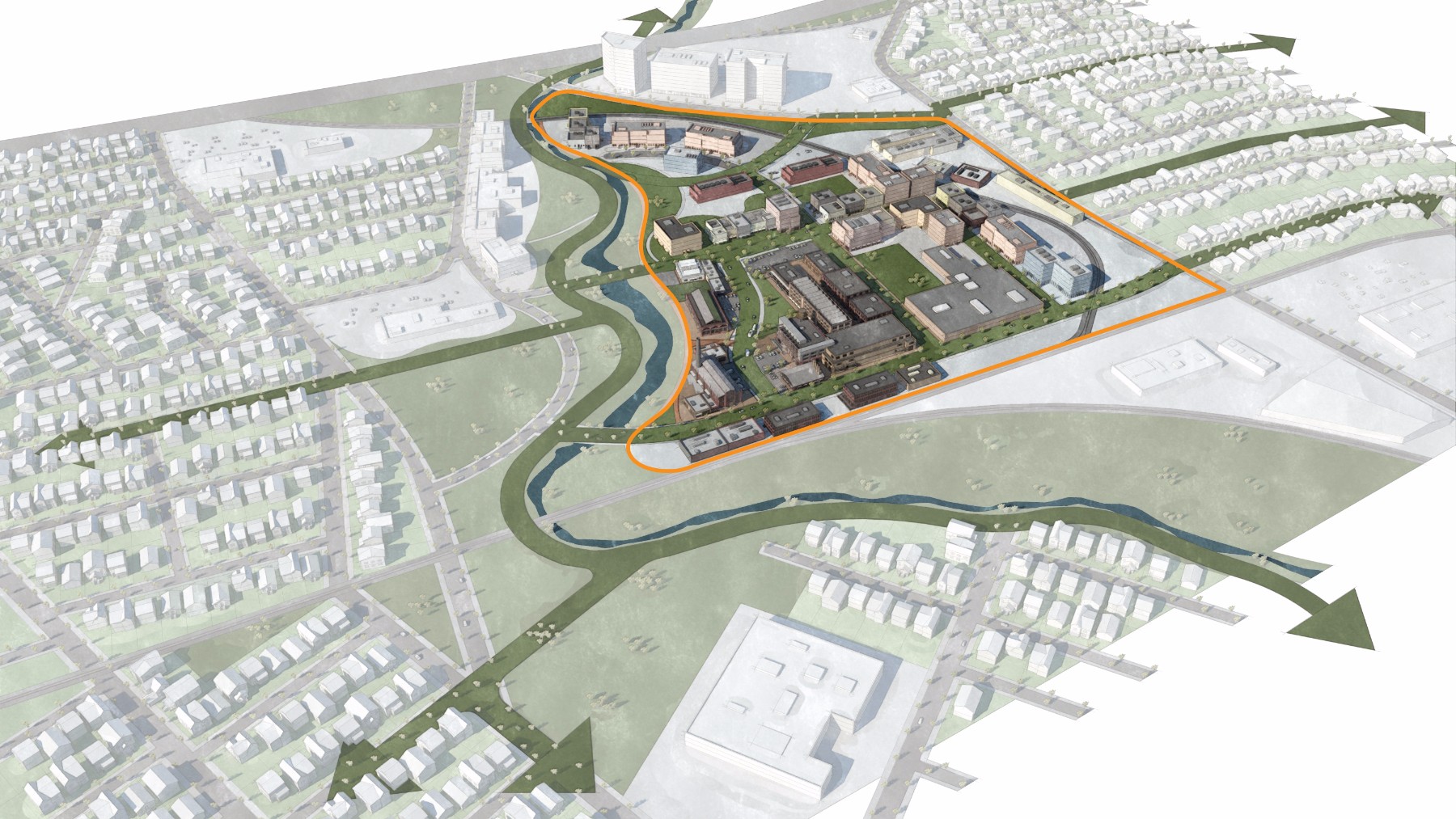
Adaptive Reuse
Industrial site adaptive reuse
Introduction
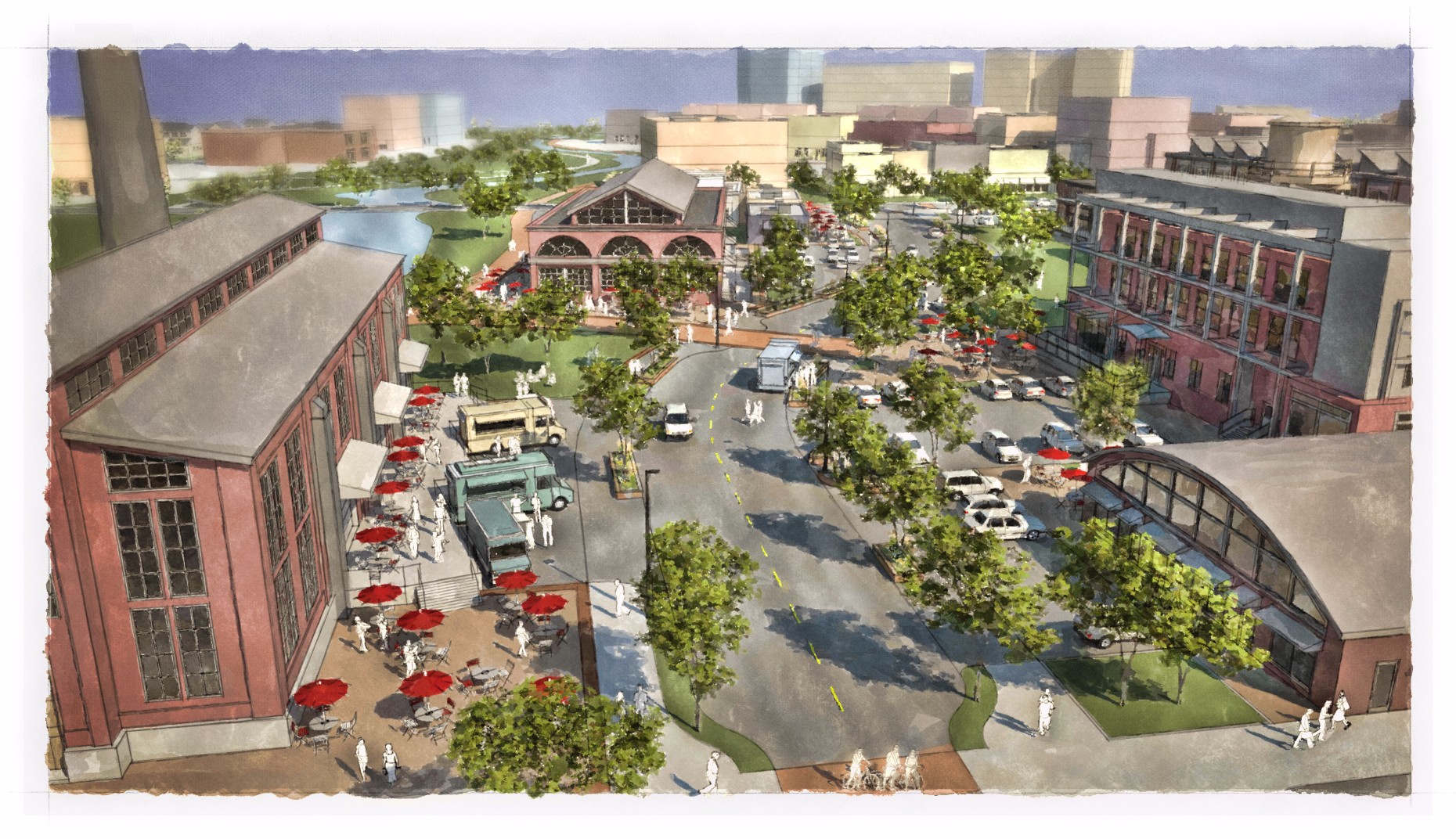
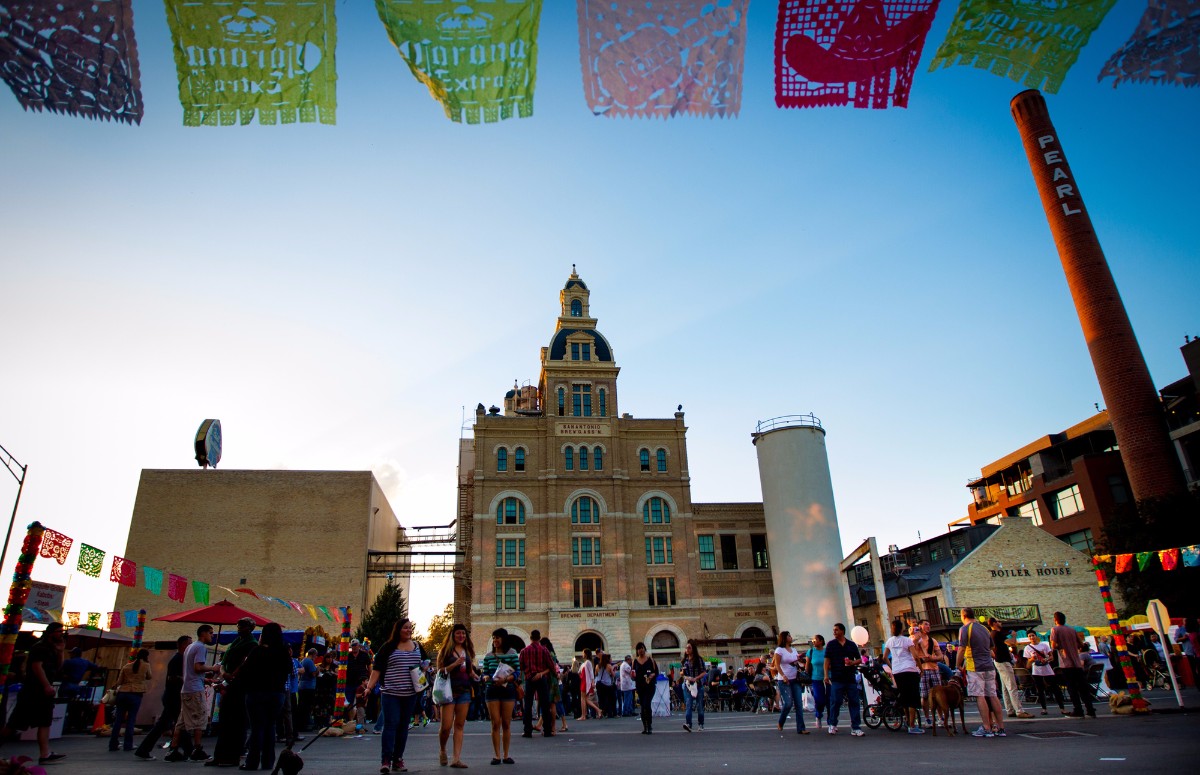
Industrial sites are some of the least activated 'places' in urban areas. Buildings typically have deep setbacks, are single-story with high ceilings, few windows and specific intended uses (such as storage or manufacturing) that are associated with very few people for the size of the buildings and properties they occupy. Industrial Site Adaptive Reuse can breathe new life into underutilized and vacant industrial sites. Key features include adaptive reuse of older industrial buildings, great public spaces and introducing a large mix of uses. High-density residential is often brought into the sites, mixing old structures and infrastructure with new uses, and integrating ample landscaping and pedestrian connectivity throughout the site. This place type is well represented by the Pearl Brewery and Blue Star developments. Future areas where this place type would work include the Lone Star Brewery site.
Major Determinant
Larger industrial site.
Relation to VIA Supportive Development Typologies
One of three typologies corresponding to VIA’s Urban Center typology.
Predominant Land Uses
Multifamily residential, office, retail, mixed-use and light manufacturing.
Performance Standards
Height: 2 to 8-story development or 35 to 110 feet
Massing and Density: 15 to 40 housing units per acre and 2:1 to 5:1 Floor Area Ratio (FAR)
Street Level Activation: Transparency along primary street of 40%; transparency along side street of 15%
Connectivity: Maximum block perimeter of 1,200 feet; minimum 90 intersections per square mile
Public Space: Plazas and park spaces totaling 10 acres per 1,000 residents
Parking: On-street and off-street parking
Potential Locations
The Industrial Site Adaptive Reuse place type is appropriate at abandoned, under-performing and outdated industrial sites. The applicability of this place type to the regional centers is addressed in the next section of this chapter.